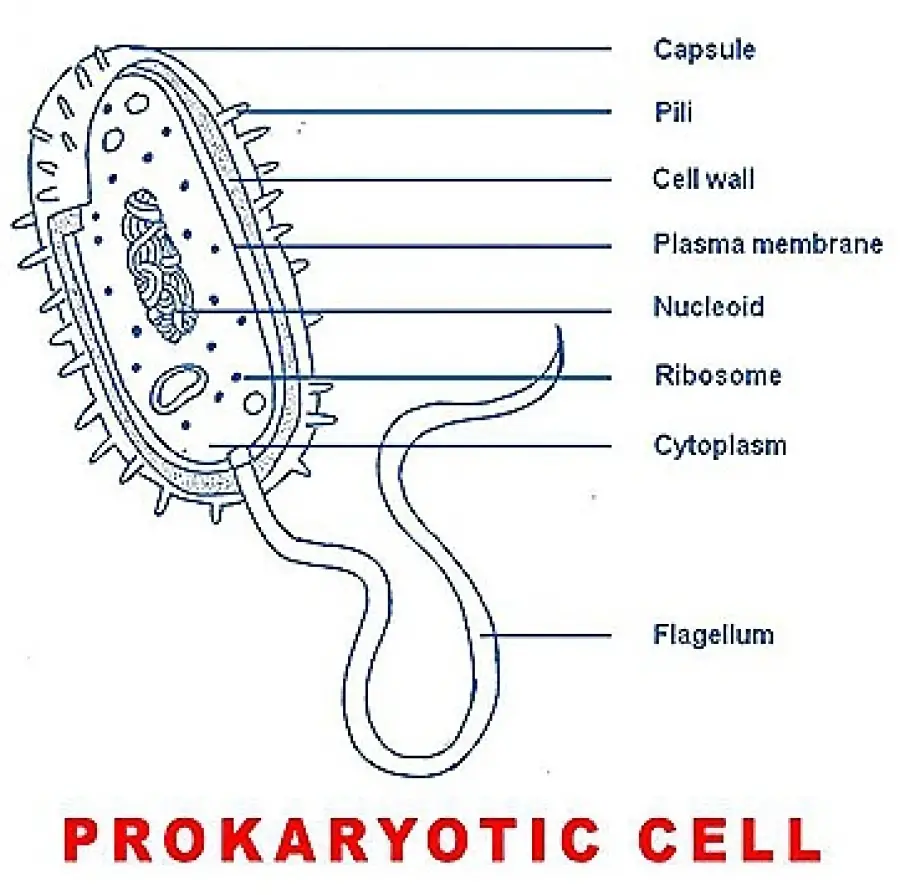
Drawing Of A Prokaryotic Cell
Drawing Of A Prokaryotic Cell - Unit 2 water, acids, and bases. All prokaryotes have chromosomal dna localized in a nucleoid, ribosomes, a cell membrane, and a cell wall. Web step by step and simple way to draw prokaryotic cell with easy methods. The plasma membrane, or cell membrane, is the phospholipid layer that surrounds the cell and protects it from the outside environment. Unit 9 more about membranes. The features of a typical prokaryotic cell are shown. Web i draw a bacterial cell to show you how to make an accurate biological drawing of a prokaryotic cell. Web distinguish between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells in terms of structure, size, and the types of organisms that have these cell types. Unit 8 membranes and transport. Web unit 1 intro to biology. What are the roles of flagella and endospores in prokaryotes? How it looks like under a microscope. Unit 5 energy and enzymes. This video explains how to draw prokaryotic cell in easy. Web many prokaryotic cells have sphere, rod, or spiral shapes (as shown below). Web what is a prokaryotic cell. Some prokaryotes may have additional structures such as a capsule, flagella, and pili. These cells are structurally simpler and smaller than their eukaryotic counterparts, the cells that make up fungi, plants, and animals. Web typical prokaryotic cells range from 0.1 to 5.0 micrometers (μm) in diameter and are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which usually have diameters ranging from 10 to 100 μm. In the following sections, we’ll walk through the structure of a prokaryotic cell, starting on the outside and moving towards the inside of the cell. Some prokaryotes may have additional structures such as a capsule, flagella, and pili. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: What are the roles of flagella and endospores in prokaryotes? Unit 6 structure of a cell. Some prokaryotes have flagella, pili, or. All cells have a plasma membrane, ribosomes, cytoplasm, and dna. Unit 8 membranes and transport. Web i draw a bacterial cell to show you how to make an accurate biological drawing of a prokaryotic cell. Web step by step and simple way to draw prokaryotic cell with easy methods. Web figure 4.5 this figure shows the generalized structure of a. Learn its structure, with diagram, facts, characteristics, parts, functions, & cell division. The other structures shown are present in some, but not all, bacteria. Web distinguish between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells in terms of structure, size, and the types of organisms that have these cell types. The word prokaryote comes from the ancient greek πρό ( pró) 'before' and. These cells are structurally simpler and smaller than their eukaryotic counterparts, the cells that make up fungi, plants, and animals. Web many prokaryotic cells have sphere, rod, or spiral shapes (as shown below). Unit 8 membranes and transport. Web what is a prokaryotic cell. How it looks like under a microscope. These neat, well labelled and colorful diagrams will make your answers look more. All cells have a plasma membrane, ribosomes, cytoplasm, and dna. What are the key features of eukaryotic cells? Some prokaryotes may have additional structures such as a capsule, flagella, and pili. Unit 6 structure of a cell. The composition of the cell wall differs significantly between the domains bacteria and archaea, the two. Web unlike eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus and complex organelles, but they have structures such as a cell wall, capsule, cytoplasm, and flagella that support their functions and survival. All prokaryotes have chromosomal dna localized in a nucleoid, ribosomes, a cell. Unit 7 more about cells. General science, 7th standard text book. Learn its structure, with diagram, facts, characteristics, parts, functions, & cell division. The features of a typical prokaryotic cell are shown. Prokaryotes include bacteria and archaea. Some prokaryotes may have additional structures such as a capsule, flagella, and pili. The features of a typical prokaryotic cell are shown. What are the roles of flagella and endospores in prokaryotes? Bacteria and archaea differ in the lipid composition of their cell membranes and the characteristics of the cell wall. Organisms within the domains bacteria and archaea are based. These neat, well labelled and colorful diagrams will make your answers look more. Some prokaryotes have flagella, pili, or. Web prokaryotic cell diagram drawing easy and step by step / how to draw and label prokaryotic cell in this video, i will learn how to draw and label a prokaryot. Describe a typical prokaryotic cell. Organisms within the domains bacteria. Here's an overview of the structures and functions of prokaryotic cells. What are the key features of eukaryotic cells? Diagram of a typical prokaryotic cell. All prokaryotes have chromosomal dna localized in a nucleoid, ribosomes, a cell membrane, and a cell wall. These cells are structurally simpler and smaller than their eukaryotic counterparts, the cells that make up fungi, plants,. What are the key features of eukaryotic cells? Unit 7 more about cells. Web unit 1 intro to biology. Some prokaryotes have flagella, pili, or. What is a prokaryotic cell? Bacteria and archaea differ in the lipid composition of their cell membranes and the characteristics of the cell wall. Web unlike eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus and complex organelles, but they have structures such as a cell wall, capsule, cytoplasm, and flagella that support their functions and survival. Web typical prokaryotic cells range from 0.1 to 5.0 micrometers (μm) in diameter and are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which usually have diameters ranging from 10 to 100 μm. Describe a typical prokaryotic cell. All cells have a plasma membrane, ribosomes, cytoplasm, and dna. Unit 6 structure of a cell. Web most prokaryotes have a cell wall that lies outside the boundary of the plasma membrane. Web identify the three most common shapes of prokaryotic cells. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have structures in common. Prokaryotic dna is found in the central part of the cell: The other structures shown are present in some, but not all, bacteria.Draw A Well Labelled Diagram Of Typical Prokaryotic Cell The Best
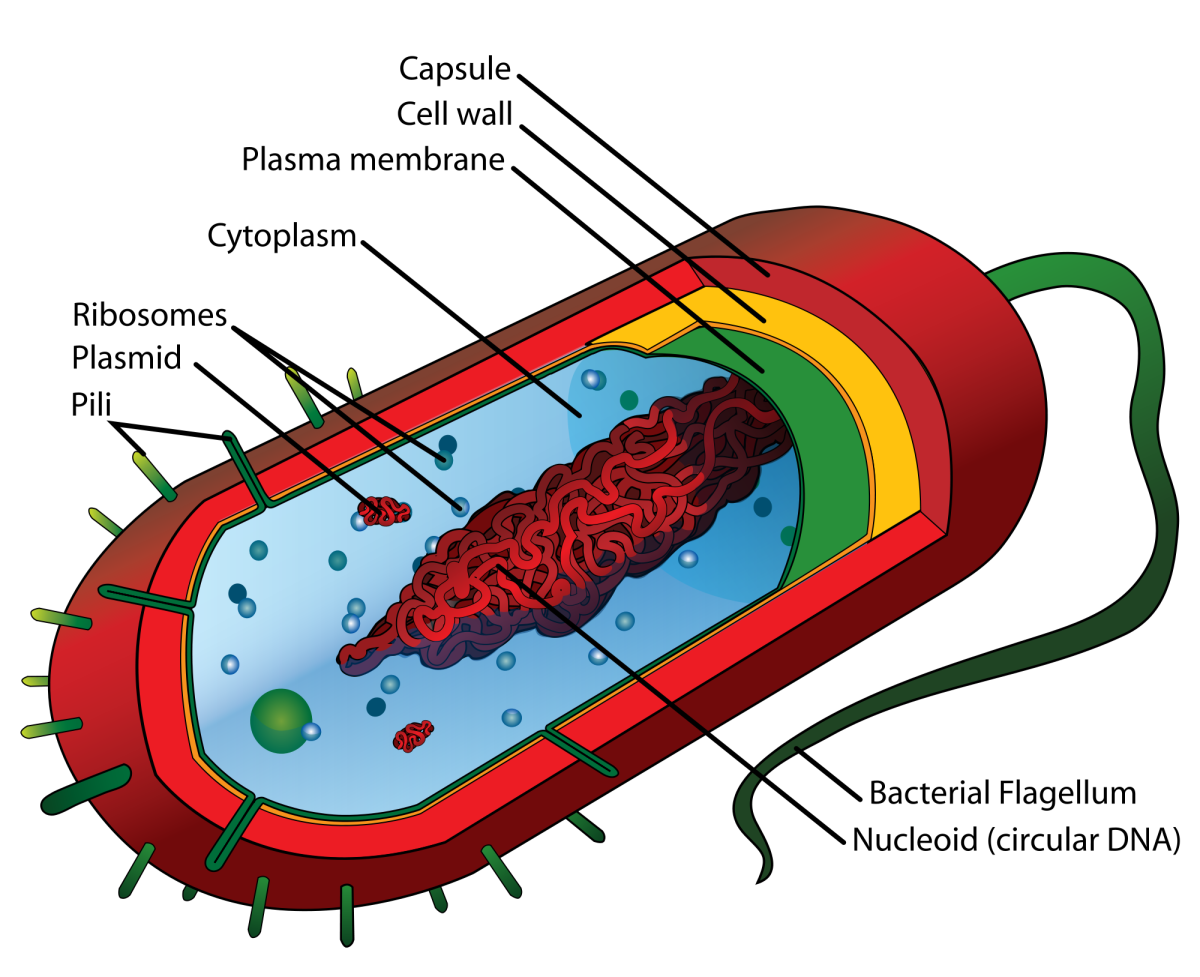
Cell Biology Glossary Cell Architecture of Prokaryotes (Bacteria
Simple Prokaryotic Cell Diagram
What's In A Cell? Library For Kids
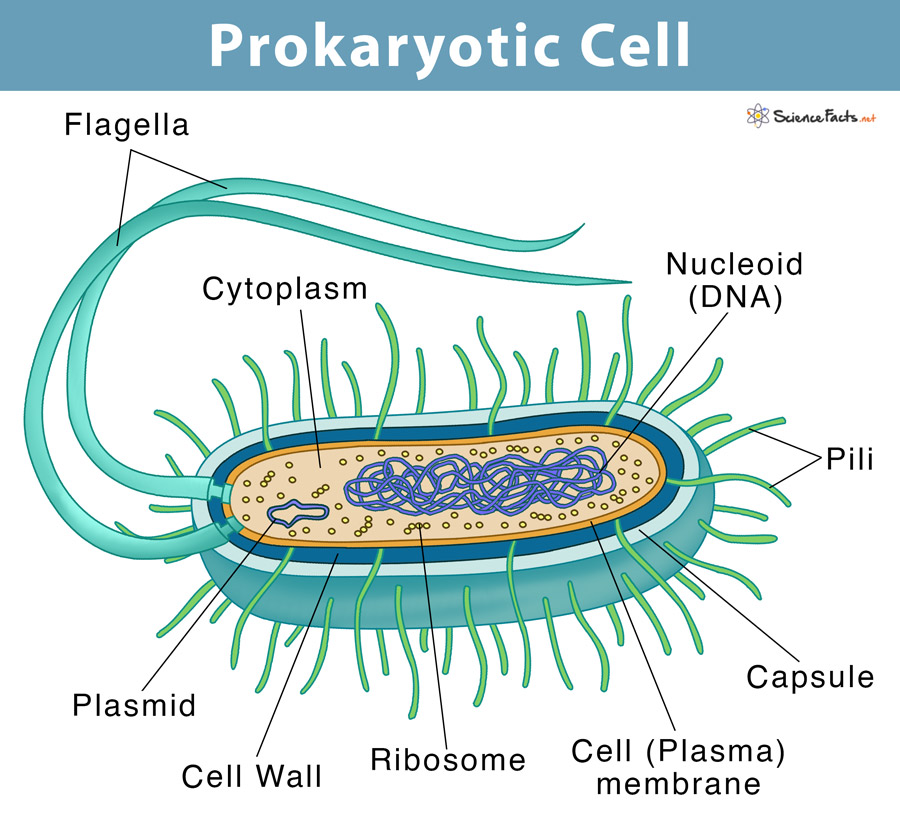
Prokaryotic Cell Definition, Examples, & Structure
Prokaryotic Cell Structure, Characteristics & Function
Prokaryotic Cell Structure A Visual Guide Owlcation
Draw a well labelled diagram of a prokaryotic cell.
Prokaryotic cell structure diagram, Stock vector Colourbox
Prokaryotic Cells Structure, Function, and Definition
Here's An Overview Of The Structures And Functions Of Prokaryotic Cells.
The Figure Below Shows The Sizes Of Prokaryotic, Bacterial, And Eukaryotic, Plant And Animal, Cells As Well As Other Molecules And Organisms On A Logarithmic.
Unit 8 Membranes And Transport.
A Darkened Region Called The Nucleoid (Figure 2).
Related Post:





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bacteria_cell_drawing-5786db0a5f9b5831b54f017c.jpg)